Cybersecurity & Data Privacy Risk Management Model (C|P-RMM)
Risks & Threats Do Not Exist In A Vacuum
It is vitally important to understand that risks and threats do not exist in a vacuum. If your cybersecurity and privacy program is appropriately built, you will have a robust controls framework where risks and threats will map directly to controls. Why is this?
- Controls are central to managing risks, threats, procedures and metrics; and
- Risks, threats, metrics and procedures need to map into the controls, which then map to standards and policies.
- Evaluates those controls based on the entity's THREAT CATALOG to identify current or potential control deficiencies; and
- Utilize the RISK CATALOG to identify the applicable risks, based on the identified control deficiencies.
SCF Threat Catalog
The threat catalog use case is: What natural and man-made threats affect control execution? (e.g., if the threat materializes, will the control function as expected?)
This use case relies on the following definition of a threat:
- Noun - A person or thing likely to cause damage or danger.
- Verb - To indicate impending damage or danger.
SCF Risk Catalog
The risk catalog use case is: What are the risks associated with a control deficiency? (e.g., if the control fails, what risk(s) is the organization exposed to?)
This use case relies on the following definition of a risk:
- Noun - A situation where someone or something valued is exposed to danger, harm or loss.**
- Verb - To expose someone or something valued to danger, harm or loss.
** Danger: state of possibly suffering harm or injury
** Harm: material / physical damage
** Loss: destruction, deprivation or inability to use
Note - Some of these risks may indicate a deficiency that could be considered a failure to meet "reasonable security practices"
| Risk Grouping | Risk # | Risk |
Description of Possible Risk Due To Control Deficiency IF THE CONTROL FAILS, RISK THAT THE ORGANIZATION IS EXPOSED TO IS: |
| Access Control | R-AC-1 | Inability to maintain individual accountability | The inability to maintain accountability (e.g., asset ownership, non-repudiation of actions or inactions, etc.). |
| R-AC-2 | Improper assignment of privileged functions | The inability to implement least privileges (e.g., Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), Privileged Account Management (PAM), etc.). | |
| R-AC-3 | Privilege escalation | The inability to restrict access to privileged functions. | |
| R-AC-4 | Unauthorized access | The inability to restrict access to only authorized individuals, groups or services. | |
| Asset Management | R-AM-1 | Lost, damaged or stolen asset(s) | Lost, damaged or stolen assets. |
| R-AM-2 | Loss of integrity through unauthorized changes | Unauthorized changes that corrupt the integrity of the system / application / service. | |
| R-AM-3 | Emergent properties and/or unintended consequences | Emergent properties and/or unintended consequences from Artificial Intelligence & Autonomous Technologies (AAT). | |
| Business Continuity | R-BC-1 | Business interruption | Increased latency, or a service outage, that negatively impact business operations. |
| R-BC-2 | Data loss / corruption | The inability to maintain the confidentiality of the data (compromise) or prevent data corruption (loss). | |
| R-BC-3 | Reduction in productivity | Diminished user productivity. | |
| R-BC-4 | Information loss / corruption or system compromise due to technical attack | A technical attack that compromises data, systems, applications or services (e.g., malware, phishing, hacking, etc.). | |
| R-BC-5 | Information loss / corruption or system compromise due to non-technical attack | A non-technical attack that compromises data, systems, applications or services (e.g., social engineering, sabotage, etc.). | |
| Exposure | R-EX-1 | Loss of revenue | A negatively impact on the ability to generate revenue (e.g., a loss of clients or an inability to generate future revenue). |
| R-EX-2 | Cancelled contract | A cancelled contract with a client or other entity for cause (e.g., failure to fulfill obligations for secure practices). | |
| R-EX-3 | Diminished competitive advantage | Diminished competitive advantage (e.g., lose market share, internal dysfunction, etc.). | |
| R-EX-4 | Diminished reputation | Diminished brand value (e.g., tarnished reputation). | |
| R-EX-5 | Fines and judgements | Financial damages due to fines and/or judgements from statutory / regulatory / contractual non-compliance. | |
| R-EX-6 | Unmitigated vulnerabilities | Unmitigated technical vulnerabilities that lack compensating controls or other mitigation actions. | |
| R-EX-7 | System compromise | A compromise of a system, application or service that affects confidentiality, integrity, availability and/or safety. | |
| Governance | R-GV-1 | Inability to support business processes | Insufficient cybersecurity and/or privacy practices that cannot securely support the organization's technologies & processes. |
| R-GV-2 | Incorrect controls scoping | Missing or incorrect cybersecurity and/or privacy controls due to incorrect or inadequate control scoping practices. | |
| R-GV-3 | Lack of roles & responsibilities | Insufficient cybersecurity and/or privacy roles & responsibilities that cannot securely support the organization's technologies & processes. | |
| R-GV-4 | Inadequate internal practices | Insufficient cybersecurity and/or privacy practices that can securely support the organization's technologies & processes. | |
| R-GV-5 | Inadequate third-party practices | Insufficient Cybersecurity Supply Chain Risk Management (C-SCRM) practices that cannot securely support the organization's technologies & processes. | |
| R-GV-6 | Lack of oversight of internal controls | The inability to demonstrate appropriate evidence of due diligence and due care in overseeing the organization's internal cybersecurity and/or privacy controls. | |
| R-GV-7 | Lack of oversight of third-party controls | The inability to demonstrate appropriate evidence of due diligence and due care in overseeing third-party cybersecurity and/or privacy controls. | |
| R-GV-8 | Illegal content or abusive action | Disruptive content or actions that negatively affect business operations (e.g., abusive content, harmful speech, threats of violence, illegal content, etc.). | |
| Incident Response | R-IR-1 | Inability to investigate / prosecute incidents | Insufficient incident response practices that prevent the organization from investigating and/or prosecuting incidents (e.g., chain of custody corruption, available sources of evidence, etc.). |
| R-IR-2 | Improper response to incidents | The inability to appropriately respond to incidents in a timely manner. | |
| R-IR-3 | Ineffective remediation actions | The inability to ensure incident response actions were correct and/or effective. | |
| R-IR-4 | Expense associated with managing a loss event | Financial repercussions from responding to an incident or loss. | |
| Situational Awareness | R-SA-1 | Inability to maintain situational awareness | The inability to detect cybersecurity and/or privacy incidents (e.g., a lack of situational awareness). |
| R-SA-2 | Lack of a security-minded workforce | The inability to appropriately educate and train personnel to foster a security-minded workforce. | |
| Supply Chain | R-SC-1 | Third-party cybersecurity exposure | Loss of Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability and/or Safety (CIAS) from third-party cybersecurity practices, vulnerabilities and/or incidents that affects the supply chain through impacted products and/or services. |
| R-SC-2 | Third-party physical security exposure | Loss of Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability and/or Safety (CIAS) from physical security exposure of third-party structures, facilities and/or other physical assets that affects the supply chain through impacted products and/or services. | |
| R-SC-3 | Third-party supply chain relationships, visibility and controls | Loss of Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability and/or Safety (CIAS) from "downstream" third-party relationships, visibility and controls that affect the supply chain through impacted products and/or services. | |
| R-SC-4 | Third-party compliance / legal exposure | The inability to maintain compliance due to third-party non-compliance, criminal acts, or other relevant legal action(s). | |
| R-SC-5 | Use of product / service | The misuse of the product / service in a manner that it was not designed or how it was approved for use. | |
| R-SC-6 | Reliance on the third-party | The inability to continue business operations, due to the reliance on the third-party product and/or service. |
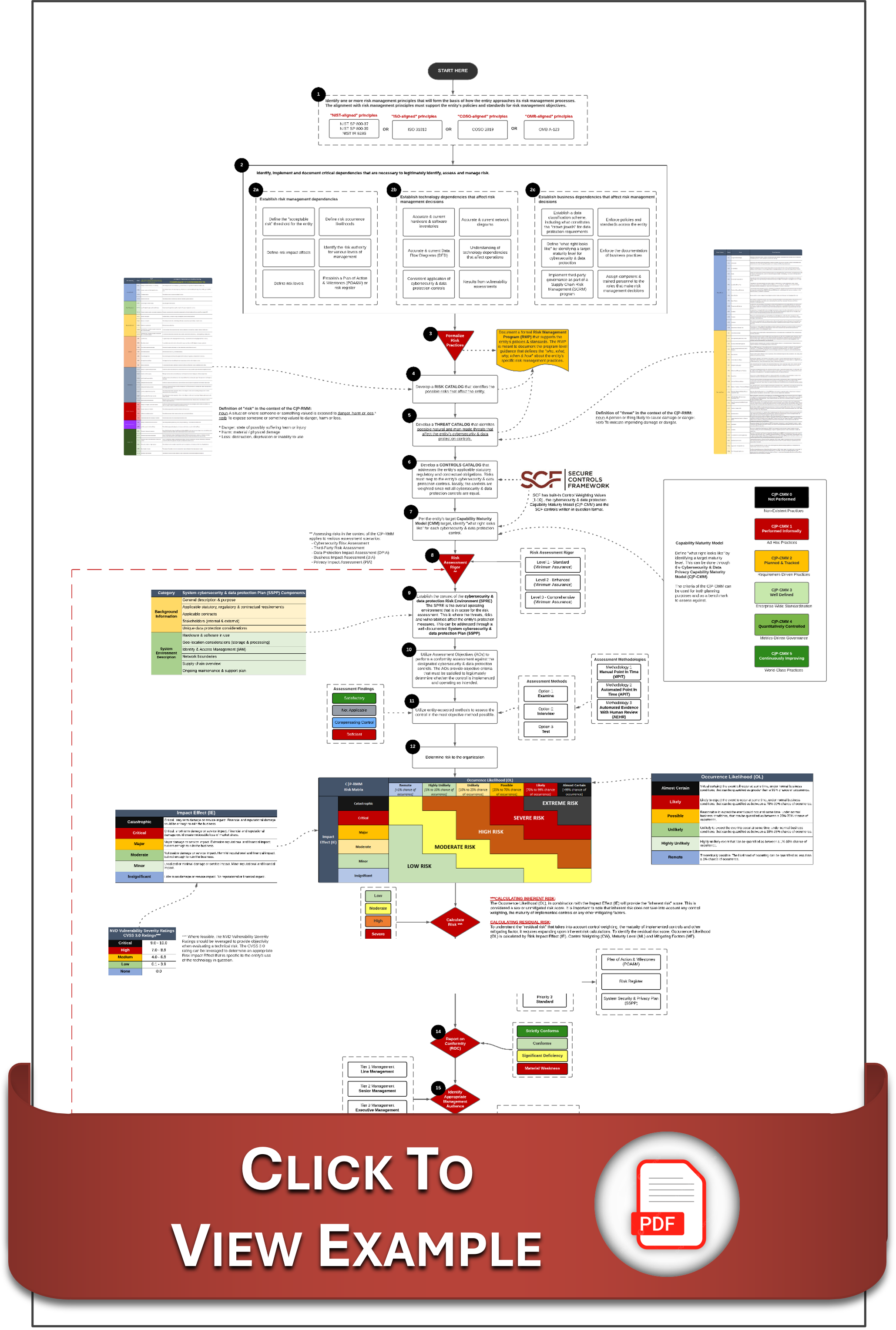
Cybersecurity & Data Privacy Risk Management Model (C|P-RMM) - "Start To Finish" Steps
The C|P-RMM breaks risk management down to seventeen (17) steps. Please download the guide for the overview and you can click on the image below for a PDF version of the C|P-RMM infographic. The C|P-RMM breaks risk management down to 16 steps. Please download the guide for the overview and you can click on the image below for a PDF version of the C|P-RMM infographic. The C|P-RMM provides a clear method to calculate both inherent and residual risk. Please download the guide for the overview and you can click on the image below for a PDF version of the C|P-RMM infographic.